Would a Supercontinent Ever Form Again?
Jurassic Flow Facts
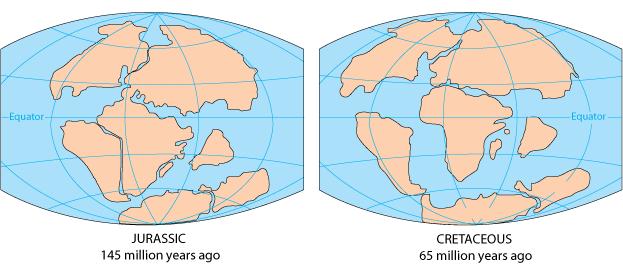
The Jurassic menstruum was the second segment of the Mesozoic era. It occurred from 201.3 1000000 to 145 meg years ago, post-obit the Triassic period and preceding the Cretaceous menstruum.
During the Jurassic period, the supercontinent Pangaea carve up autonomously. The northern half, known as Laurentia, was splitting into landmasses that would eventually form N America and Eurasia, opening basins for the central Atlantic and the Gulf of United mexican states. The southern half, Gondwana, was drifting into an eastern segment that would form Antarctica, Madagascar, Bharat and Australia, and a western portion that would form Africa and South America. This rifting, forth with mostly warmer global temperatures, immune for diversification and authorisation of the reptiles known as dinosaurs.
Plant life
By the Mesozoic era, living things had evolved the capability of living on the land rather than being confined to the oceans. By the offset of the Jurassic, plant life had evolved from Bryophytes, the low-growing mosses and liverworts that lacked vascular tissue and were confined to swampy moist areas.
Ferns and gingkoes, complete with roots and vascular tissue to move water and nutrients and a spore system of reproduction, were the dominant plants of the early Jurassic. During the Jurassic, a new method of constitute reproduction evolved. Gymnosperms, cone-bearing plants such as conifers, immune for air current distribution of pollen. This bisexual reproduction allowed for greater genetic combination and by the end of the Jurassic, the gymnosperms were widespread.
Fossil evidence has as well revealed that angiosperms, or flowering plants, as well emerged in the mid to late Jurassic. Previously, paleobotanists had assumed that angiosperms did non evolve until the Cretaceous catamenia. However, flowering plants would take remained rare compared with gymnosperms during the Jurassic.
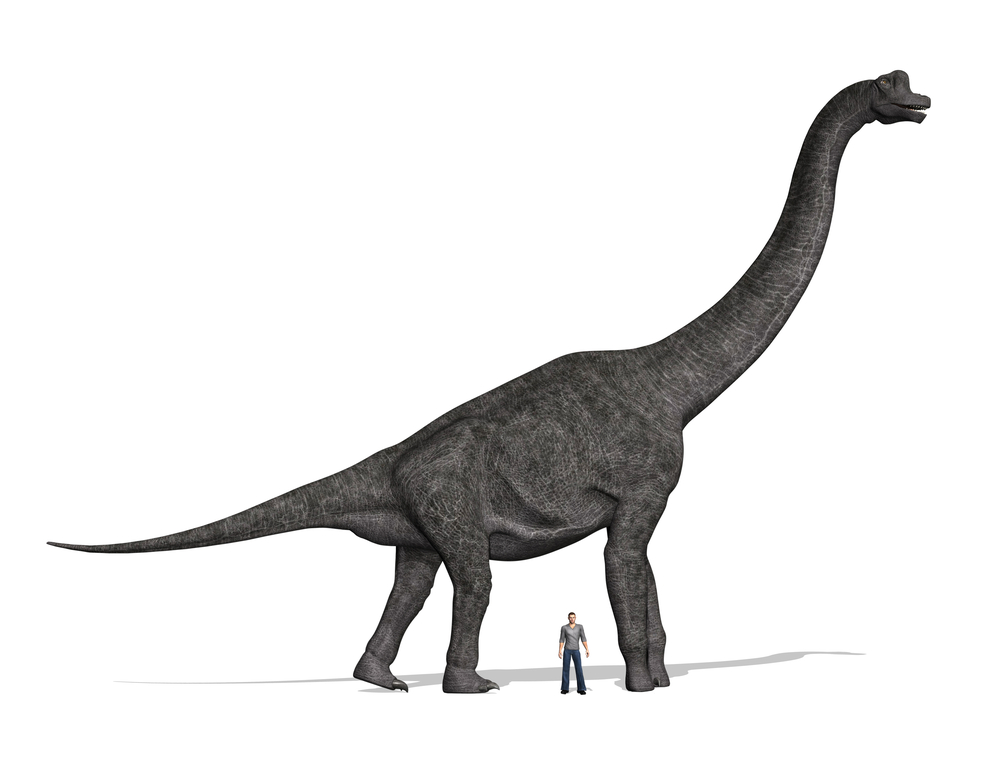

Age of the dinosaurs
As Steven Spielberg's 1993 film "Jurassic Park" asserts, reptiles were the dominant animal life forms during the Jurassic menstruum. Reptiles had overcome the evolutionary hurdles of support and reproduction that express the amphibians. Reptiles had strong ossified skeletons supported by advanced muscular systems for body support and locomotion. Some of the largest animals ever to live were dinosaurs of the Jurassic menstruum. Reptiles were too capable of laying amniotic eggs, which kept the developing young moist and nourished during gestation. This allowed for the starting time fully terrestrial animal life cycles.
Sauropods, the "lizard hipped" dinosaurs, were herbivorous quadrupeds with long necks balanced by heavy tails. Many, such as Brachiosaurus, were huge. Some genera obtained lengths greater than 100 feet and weights over 100 tons, making them the largest land animals ever to walk the earth. Their skulls were relatively small, with nostrils carried high virtually their eyes. Such modest skulls meant that they had very small-scale brains as well. Despite the small brains, this grouping was very successful during the Jurassic flow and had a wide geographic distribution. Sauropod fossils take been institute on every continent, even Antarctica. Other well-known dinosaurs of the Jurassic include the plated Stegosaurus and the twoscore-pes-alpine (12 meters) Giraffatitan, likely the tallest dinosaur that ever lived.
Carnosaurus ways "meat-eating dinosaur." With such large herbivorous prey animals, it makes sense that big predators were likewise common. Allosaurus was one of the most common Carnosaurs in Due north America; numerous intact skeletons have been found in the fossil beds of Utah. Allosaurus was superficially like to the later evolving Tyrannosaurus rex, although cladistic analysis shows them to exist simply distantly related. Allosaurus was a bit smaller with a longer jaw and heavier forelimbs. They relied on the stronger hind limbs for a running gait, but it is unclear how fast they could move.
Information technology is unlikely to take been common for an Allosaurus to have on a healthy big adult herbivore like a Brachiosaurus or even a Stegosaurus. They were likely opportunistic, consuming young, sick, anile or injured prey. They were probably able to grasp such casualty with their heavily muscled forelimbs, tearing it to pieces with large claws so swallowing the pieces whole.
Early on mammals
Dinosaurs may have been the dominant land animals, but they were non solitary. Early mammals were more often than not very small herbivores or insectivores and were not in contest with the larger reptiles. Adelobasileus, a shrew-like brute, had the differentiated ear and jaw bones of a mammal and dates from the late Triassic.

In August 2011, scientists in China announced discovery of Juramaia. This tiny animal of the mid-Jurassic has caused excitement amid scientists because it is clearly a eutherian, an ancestor of placental mammals, indicating that mammals evolved much earlier than previously thought.
Marine life
Marine life of the Jurassic flow was likewise highly diversified. The largest marine carnivores were the Plesiosaurs. These carnivorous marine reptiles typically had wide bodies and long necks with iv flipper shaped limbs. Ichthyosaurus was a more than fish-shaped reptile that was most common in the early Jurassic. Considering some fossils take been constitute with smaller individuals that appear to take been inside the larger ones information technology is hypothesized that these animals may take been among the first to take internal gestation and bear alive young. Cephalopod ancestors of mod squid and finned relatives of modern sharks and rays were also common. Amid the near cute fossils of marine life were left by the spiral shells of the ammonites.
Editor's notation: Updated on April 17, 2013 to correct descriptions of life during the Mesozoic era and of the Juramaia.
Originally published on Alive Science.
Source: https://www.livescience.com/28739-jurassic-period.html
0 Response to "Would a Supercontinent Ever Form Again?"
Post a Comment